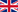
The melon fly (Bactrocera cucurbitae) is a fruit fly of the family Tephritidae. It is a serious agricultural pest, particularly in AFRICA.
The melon fly is considered the most destructive pest of melons and other related crops. In Tanzania, it has caused serious damaged to melon, cucumber and tomato crops.The melon fly can attack flowers, stem, root tissue, and fruit.Melon flies use at least 125 host plants. They are major pests of beans, bittermelon, wintermelon, cucumbers, eggplant, green beans, hyotan, luffa, melons, peppers, pumpkins, squashes, togan, tomatoes, watermelon, and zucchini
One of the biggest challenges in farming watermelon is controlling the bactocera cucubitae. In fact, if not managed, it can cause up to 80% crop loss. Ignore it at your own peril. Therefore, how does a farmer protect their crop?
Adult fly
The adult melon fly is 6 to 8 mm in length. Distinctive characteristics include its wing pattern, its long third antennal segment, the reddish yellow dorsum of the thorax with light yellow markings, and the yellowish head with black spots.
Egg
The egg is elliptical, about 2 mm long, and pure white. It is almost flat on the ventral surface, and more convex on the dorsal. Eggs are often somewhat longitudinally curved.
Larva
The larva is a cylindrical-maggot shape, elongated, with the anterior end narrowed a somewhat curved ventrally. It has anterior mouth hooks, ventral fusiform areas and a flattened caudal end. Last instar larvae range from 7.5 to 11.8 mm in length. The venter has fusiform areas on segments 2 through 11. The anterior buccal carinae are usually 18 to 20 in number. The anterior spiracles are slightly convex in lateral view, with relatively small tubules averaging 18 to 20 in number.
Pupa
The puparium ranges in color from dull red or brownish yellow to dull white, and is about 5 to 6 mm in length.
1) Chemical control
This is the most popular method of control. It works by mimicking nature. Firstly, for reproduction to take place, the female secretes sex pheromones to attract the male. Therefore, using this biological trait, a vial is steeped in the attractant to lure the male fly.It is combined with an insecticide.The male fly is attracted by the scent and ends up being captured in the trap. By eliminating the male, there will be no mating. Consequently, no eggs will be hatched. Eventually, the population of the fruit fly will be managed. Scientifically, it is called the male annihilation technique.
To ensure its efficacy, use 4-5 traps per acre. While installing, the trap should face the north of the plant. Additionally, the trap should be put 1 foot above the ground. This ensures the scent is carried further and attracts the males. Every 75 days the trap should be emptied. As for the wick, it is best to change after 75 days. However, in hotter climates it should be changed after 75 days.Currently, in the market we have the trap from kangeta kilimo.
2) Protein food bait
Whereas, the male annihilation technique targets the male, the protein food bait method focuses on the female. For the young female fruit fly to reach sexual maturity it has to feed on protein. It will also need it to develop eggs. They feed on protein found in the leaf and the fruit surface.When the female start to lay eggs they stop consuming protein. Just like the male annihilation technique, this method targets the behavior of the female. In this method a protein laced with a soft toxin is used to kill the fly. This method prevents the female from laying eggs. Hence, the population of the fruit fly is controlled.Notably, at least two thirds of the captured insects are female and the other third are male.
For an acre, you will need 30 traps. The spacing from trap to trap should be 10 meters. The trap should be filled with 400 ml of the solution. Collect the catches every week and sieve. Just like the pheromone trap the changing of the solution should be done after 14 days. If there is a high rate of evaporation change the liquid after 7 days.
3) Bio pesticides
Unfortunately, the over reliance on synthetic pesticides has caused pesticide resistance in many parts of the world. The melon fly is no different.The use of bio pesticides derived from fungi can help the situation. Metarhizium anisopliae is a form of fungus that occurs naturally in the soil. The fungi isolate strain 69 can be used to control the melon fly.
These fungi can be used as a soil inoculant or a spray. When applied to the soil, the granules of the fungi are raked in before fruiting. Since the pupae burrow in the soil before they mature into adults the fungi will kill them before they morph into adults.
The other way of using the fungi is through an oil based spray. When sprayed the fungus spores bind to the exoskeleton of the bactocerafruit fly. Once the fungus enters the insect it grows rapidly and it dies. Insects that come into contact with the infected insect also become infected and die.
4) Cultural control
To bolster the aforementioned methods, cultural control is important as well. This can be done through field sanitation and planting a trap crop.While starting your season plant a border crop like maize that will serve as the host plant for pests. The crop will also help in managing aphids; another troublesome pest in watermelon.
For the infected fruit ensure it is collected and destroyed. The fruit should be put in a plastic bag to kill the fruit fly maggots or they be buried in a 3 feet deep hole. Add lime to kill the larvae. This should be done at least twice a week.Finally, rotate the watermelon with non host crops (non cucurbits) for at least 3 seasons before planting again in the same spot. Ultimately, there should be no build up of pests.
Conclusion
The choice of control will depend on the level of infestation, method of production (organic or inorganic), and costs. It is best to start control at flowering i.e. week 4. Strive for prevention to stop any economic injury. In conclusion, always seek for an integrated pest management approach. It is more chilled out on the environment.